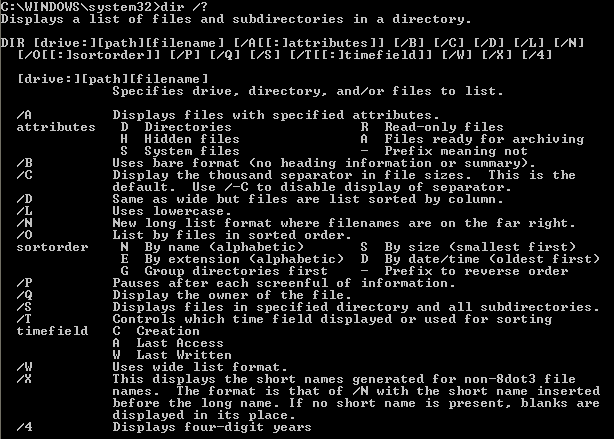
Command Prompt Commands
Command-line-commands A lightweight module to help build a git-like command interface for your app. Its job is to extract the command (the first argument, unless it's an option), check it's valid and either return it or throw. From there, you can parse the remaining args using your preferred option parser (e.g., etc.). Synopsis Create a list of valid commands ( null represents 'no command'). Supply it to commandLineCommands, receiving back an object with two properties: command (the supplied command) and argv (the remainder of the command line args). Log ( ' argv:%s ', JSON. Stringify ( argv ) ) We'll assume the above script is installed as example.
Since the validCommands list includes null, running it without a command is valid: $ example command: null argv: Running example with no command and one option: $ example -verbose command: null argv: '-verbose' Running example with both a command and an option: $ example install -save something command: install argv: '-save','something' Running example without a valid command will cause commandLineCommands to throw. From here, you can make a decision how to proceed based on the command and argv received. For example, if no command ( null) was passed, you could parse the remaining argv for general options (in this case using ).
Const commandLineCommands = require ( ' command-line-commands ' ) commandLineCommands(commands, argv) ⇒ Object ⏏ Parses the argv value supplied (or process.argv by default), extracting and returning the command and remainder of argv. The command will be the first value in the argv array unless it is an option (e.g. Kind: Exported function Throws:. INVALIDCOMMAND - user supplied a command not specified in commands.
Command Prompt does requires some commands and key combinations to remember to use it properly. If you are willing to spend some time to learn a few handy tricks, your productivity can sky rocket. Command Prompt has tons of tricks with over 280 commands, but learning all the tricks and commands might not be necessary. Spaces and symbols such as a '/' or a '-' may be used to allow the command processor to parse the command line into filenames, file specifications, and other options. The command interpreter preserves the case of whatever parameters are passed to commands, but the command names themselves and file names are case-insensitive.
Command Prompt Commands
Param Type Description commands string Array. One or more command strings, one of which the user must supply. Include null to represent 'no command' (effectively making a command optional).
argv Array. An argv array, defaults to the global process.argv if not supplied.
© 2015-17 Lloyd Brookes.
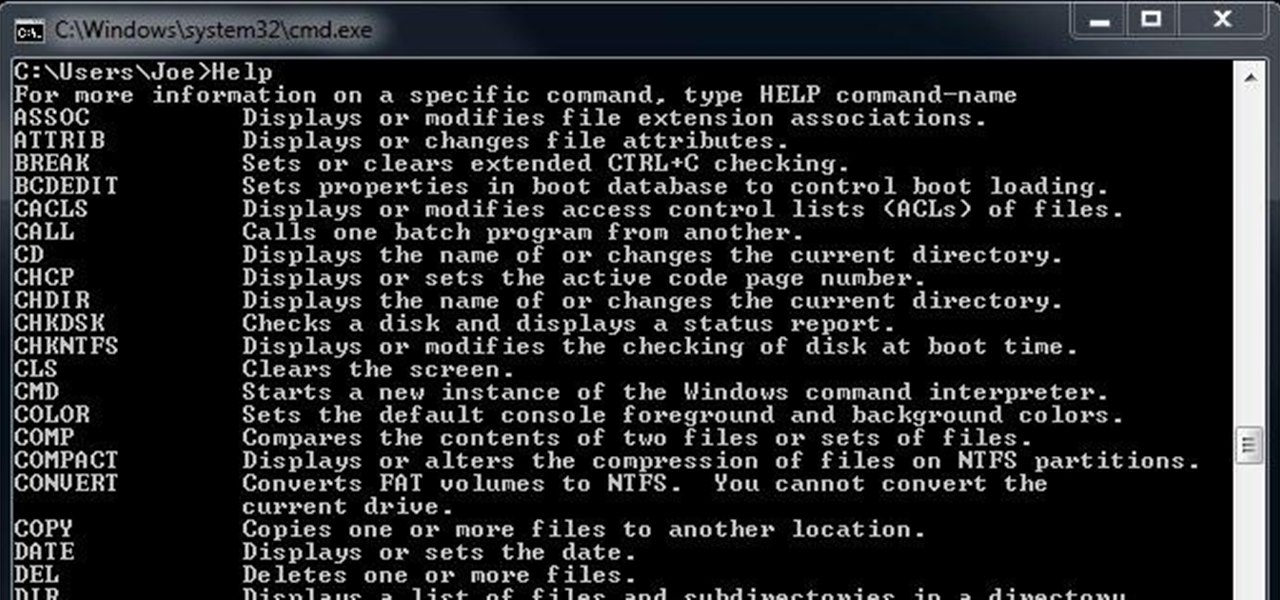
Here are my top 10 favorite command-line commands for Windows 7. Each command is native on the operating system so you don't need special software.
Administrative access may be required for some of them. Checking the IP addresses on the local system One of the most frequently used command by IT professionals is ipconfig /all, which displays the active Internet Protocol (IP) addresses, Media Access Control (MAC) address, default gateway, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) status and more for each network interface on the computer. Ipconfig /all Related commands:. ipconfig /release - releases currently assigned IP addresses. ipconfig /renew - acquires IP addresses from a DHCP server 2. Clearing the DNS cache on the local computer The ipconfig /flushdns command clears the domain name server (DNS) cache stored on the local computer.
It's often used when the internal network or external resources can't be accessed because of corrupted DNS data. Ipconfig /flushdns Related commands:. ipconfig /displaydns - displays the current DNS cache. net start (or stop) dnscache - turns on (or off) the local DNS cache client, flushing the DNS cache.
Turning off the cache allows the system to resolve addresses: Each address will be resolved each time a request is made, rather than saving the IP address for that host. Querying group policy settings Group policy settings determine how the computer is configured for system and user settings. Because these settings can be configured centrally from a domain controller - as well as locally from the computer itself - determining the actual 'in-use' policy can be tricky. The gpresult /r command displays the 'resultant set of policy,' including when the policies were last processed and the actual settings for computer and user policies. Gpresult /R For remote computers: gpresult /S computername /U username /P password /R Related commands:. gpresult /H filename.html - creates an HTML-formatted view of the group policy settings 4. Refreshing group policy settings Changing group policy settings on the domain controller allows endpoint systems to receive the updates the next time they refresh their policy - anywhere from 20 to 90 minutes later.
To speed up this process and obtain the new settings immediately, force the update with this command gpupdate /force 5. Shutting down a computer When performing systems management routines such as installing patches, it may be necessary to shut down and/or restart the system in a scripted manner. The shutdown command will turn off a local or remote computer - giving one minute's notice to the logged on user. Shutdown /s For remote computers: shutdown /m computername /s Related commands:. shutdown /r - performs shutdown and restart. shutdown /a - aborts a shutdown.
shutdown /r /t 120 /c 'Shutting Down for maintenance' /f /d p:4:1 - performs a shutdown in 120 seconds, gives a message to the user, forces applications closed and notes the shutdown reason in the event log 6. Query the audit settings The auditpol command can query and set audit settings on the local computer. For security auditing, it can be very useful to run this command on each machine and review the results. Auditpol /get /category:. Related commands:. auditpol /get /category:. /r - outputs results to CSV format 7.
Perform a Windows Update check in The client typically checks in with Microsoft (or a local Windows Server Update Services server) every 22 hours. If you want to force a check-in sooner, run the following command. Note: This command-line script does not give any user feedback to the screen.
Wuauclt /detectnow 8. Query the status of services Use the to see the services installed on a computer and if they are currently active. Sc query state= all For remote computers: sc computername query state= all Related commands:. sc query servicename - queries a specific service. sc qc servicename - obtains configuration information for a specific service. sc computername stop servicename - stops a service on a remote computer.
sc computername start servicename - starts a services on a remote computer 9. Query the status of the Windows Firewall Windows Firewall has different settings for different connection types - a public profile for when you're connected to the Internet, a private profile for when you're connected to an internal network, and a domain profile when you're connected to the corporate network. It's important to understand which firewall settings are in use for each profile. Netsh advfirewall show allprofiles For remote computers: netsh -r computername advfirewall show allprofiles ( Note: Remote registry access must be available on the remote computer for this command to work.) Related commands:. netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off - turns off the firewall for all states. netsh -r computername advfirewall set publicprofile state on - turns on the remote computer's firewall for the public profile.
netsh -r computername advfirewall set privateprofile state off - turns off the remote computer's firewall for the private profile. Execute a command against a group of computers With the FOR command, you can execute commands against a series of computers or IP addresses.
This can be a useful way to perform scripted actions against remote computers in a large network space. To query the firewall state for all computers in a Class C network and save results to individual filenames, enter the following: FOR /L%i IN (1,1,254) DO netsh -r 192.168.1.%i advfirewall show allprofiles 192.168.1.%i.firewallstate.txt Substitute your favorite remote command-line commands in place of the netsh command above.
Example: FOR /L%i IN (1,1,254) DO gpresult /S 192.168.1.%i /F /H 192.168.1.%i.gpresult.html For more information about any of the above commands, type the command at the command-line followed by /? About the author: Eric Schultze is a principal product manager at Amazon Web Services.
Prior to Amazon, Schultze worked at Microsoft, where he helped manage the security bulletin and patch-release process. Schultze likes to forget that he used to work as an internal auditor on Wall Street.